At its heart, 4K video resolution refers to a display that packs in approximately 4,000 horizontal pixels, creating an incredibly sharp and detailed picture. This format, which you'll often see labeled as Ultra High Definition (UHD), has four times the pixel density of the old standard, 1080p Full HD. The result is a much more vibrant and lifelike image.
Decoding The Pixels Behind 4K
Think of a video screen as a giant mosaic made of tiny colored tiles. A standard 1080p HD video uses around 2 million of these tiles (pixels) to assemble the final picture. When you jump up to 4K, you're looking at a massive upgrade to over 8 million pixels.
This exponential increase in "tiles" is what allows for far more intricate detail and clarity. For example, imagine watching a nature documentary. In 1080p, a wide shot of a forest might show a green canopy. In 4K, that same shot reveals individual leaves, the texture of the bark on distant trees, and even subtle movements of wildlife you would have otherwise missed.
Specifically, consumer 4K resolution is 3840 pixels horizontally by 2160 pixels vertically, which is why it's also commonly called 2160p. Packing more pixels into the same screen area means each individual pixel is smaller. This is key because it gets rid of that blocky, grid-like look you might notice on lower-resolution screens, especially when you're sitting close or watching on a large TV.
Comparing Common Video Resolutions At a Glance
To put 4K in perspective, it helps to see how it stacks up against other common resolutions. This table gives a quick rundown of the most familiar standards.
| Resolution Standard | Pixel Dimensions | Total Pixels (Approx.) |
|---|---|---|
| HD (720p) | 1280 x 720 | 921,600 |
| Full HD (1080p) | 1920 x 1080 | 2.1 Million |
| Quad HD (1440p/QHD) | 2560 x 1440 | 3.7 Million |
| Ultra HD (4K/2160p) | 3840 x 2160 | 8.3 Million |
| Full Ultra HD (8K) | 7680 x 4320 | 33.2 Million |
As you can see, the leap from 1080p to 4K isn't just a small step—it's a massive jump in visual information.
Why More Pixels Matter
So, what's the practical benefit of all this pixel-packing? A much more immersive viewing experience. Details that would be blurry or completely lost in 1080p—like the fine texture of a piece of clothing, individual leaves on a distant tree, or small text on a sign—are rendered with crisp precision in 4K.
This visual gives a great sense of just how big the jump is from 1080p to 4K.
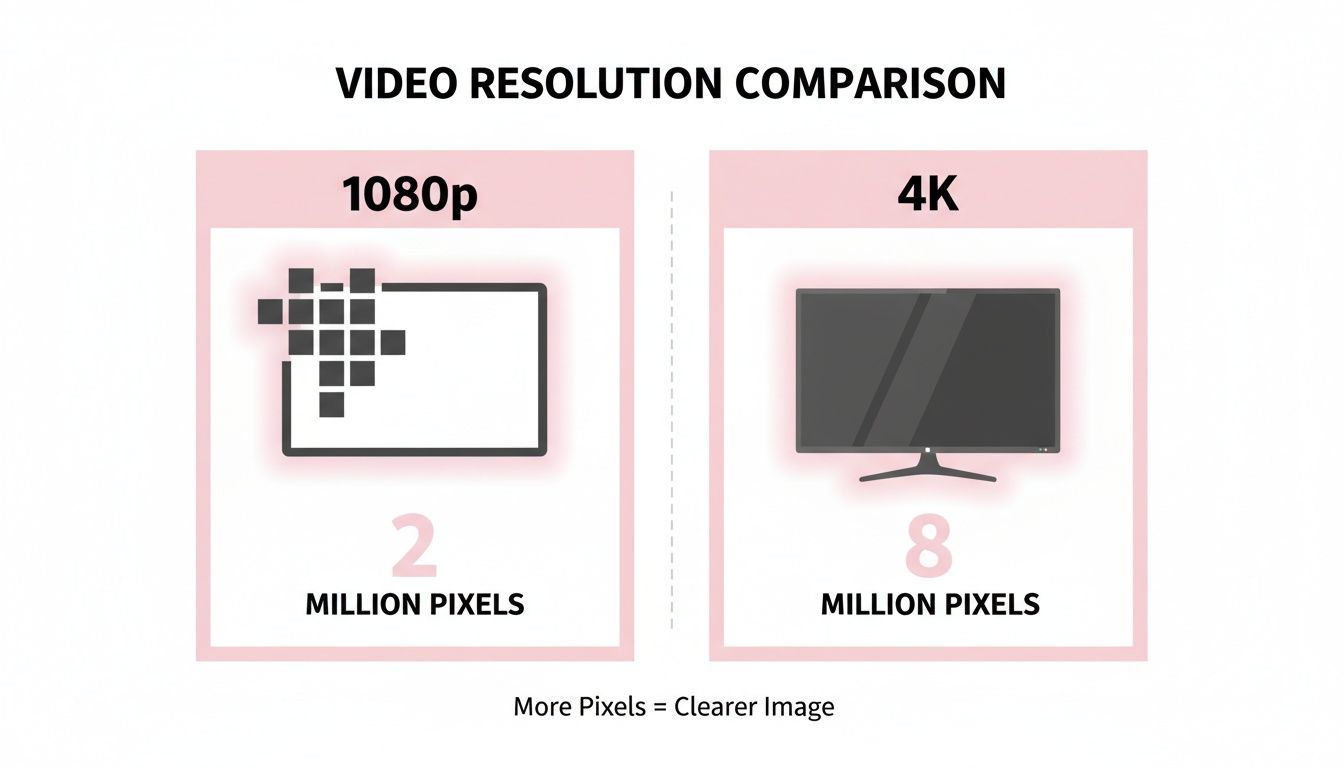
As the infographic makes clear, moving from two million to over eight million pixels is exactly what gives 4K its signature clarity.
The real magic of 4K isn't just about a bigger number. It’s about presenting images with a depth and realism that pulls you in, making you feel like you're looking through a window rather than at a screen.
Of course, resolution is just one piece of the puzzle. As screens evolve, we see combinations like QHD resolution and 120Hz displays that pair pixel density with high refresh rates for even smoother motion. Understanding this foundation of pixel count is the first step to appreciating why 4K has become the modern standard for high-quality video.
The Journey from Standard Definition to Ultra HD
The concept of 4K resolution didn't just pop up out of nowhere. It's the latest stop on a long road of technological progress, taking us from the fuzzy, boxy screens of yesterday to the incredibly sharp displays we have today. This whole evolution was pushed forward by better camera sensors, more powerful processors, and of course, the ever-improving screens in our living rooms.
Not too long ago, Standard Definition (SD) was all there was. Clocking in at a mere 640 x 480 pixels, SD video looks blurry and indistinct to our modern eyes. It was perfectly fine for the old CRT televisions it was designed for, but technology rarely stands still.

The Leap to High Definition
The first massive jump in quality came with High Definition (HD). This upgrade introduced two main standards that became household names: 720p (1280 x 720) and the even better 1080p (1920 x 1080), which we know as Full HD.
With over two million pixels, 1080p delivered a dramatically sharper and wider picture that was a perfect fit for the new widescreen flat-panel TVs hitting the market. For years, 1080p was the undisputed king of quality for broadcast TV, Blu-ray discs, and the early days of online streaming. But the push for more detail was already underway.
The Rise of Ultra HD and the 4K Standard
The next evolutionary step was a big one, ushering us into the era of Ultra High Definition (UHD), more commonly known as 4K. This wasn't just a minor improvement; it was a fundamental change in how much detail could be packed into a screen.
So, how big is the leap? Consumer 4K UHD boasts a resolution of 3840 x 2160 pixels. That’s a jaw-dropping four times the total number of pixels as 1080p. We’re talking about 8.3 million pixels creating the image, compared to just over 2 million for Full HD. This massive increase in pixel density is what gives 4K its incredible clarity and depth. You can explore the technical nuances of various resolutions to see how these standards stack up.
It’s also helpful to know that "4K" can mean two slightly different things, which sometimes causes a bit of confusion.
- Consumer UHD (3840 x 2160): This is the 4K you see everywhere—on TVs, streaming services like Netflix, and most cameras you can buy. It sticks to the familiar 16:9 widescreen aspect ratio.
- DCI 4K (4096 x 2160): This is the professional cinema standard. It’s a bit wider, giving filmmakers extra room to crop and reframe shots during post-production without losing quality.
Key Takeaway: The evolution from SD to 4K isn't just a numbers game. It's about making the viewing experience more immersive and realistic, turning the screen from a simple display into a window on another world.
Understanding this history shows that 4K isn't just a marketing buzzword. It's a genuine milestone in visual technology that has set a new benchmark for quality, shaping everything from blockbuster movies to the videos on our phones.
Why a Great 4K Image Is More Than Just Pixels
Having over eight million pixels is a fantastic starting point, but it's only one piece of the puzzle. Think of pixel count as the sheer size of your canvas. To create a masterpiece, you also need high-quality paint (bitrate), fluid brushstrokes (frame rate), and a massive palette of colors (color depth).
These other factors are what truly separate a genuinely professional 4K experience from a merely high-resolution one. In fact, a 4K video with a low bitrate and a choppy frame rate can easily look worse than a well-produced 1080p video. Getting a handle on these components is non-negotiable for anyone serious about creating or delivering top-tier content.
The Role of Frame Rate in Smooth Motion
Frame rate, measured in frames per second (fps), is simply how many individual images are flashed on your screen every second to create the illusion of movement. When the frame rate is too low, motion looks jerky and unnatural. A higher frame rate, on the other hand, delivers that buttery-smooth look we all love.
- 24fps: This is the long-standing cinematic standard. It's what gives movies that classic, film-like feel.
- 30fps: You'll find this used for most broadcast television and a ton of online videos. It provides a clean, standard look that audiences are very familiar with.
- 60fps or higher: This is where things get exciting. It’s perfect for fast-paced content like sports, video games, or high-octane action sequences. The extra frames make motion appear incredibly fluid and lifelike, which is critical for capturing crisp detail when things are moving quickly.
A live sports broadcast in 4K at 60fps, for example, lets you track a speeding baseball without it turning into a blurry streak—a detail that would be completely lost at 24fps. That smoothness is what makes the experience so much more immersive.
Bitrate: The Data Behind the Detail
If frame rate is all about smoothness, bitrate is all about clarity. At its core, bitrate is the amount of data used to encode one second of video, usually measured in megabits per second (Mbps). The higher the bitrate, the more data is preserved, which translates to a cleaner, more detailed image with fewer ugly compression artifacts.
Think about sending a photo over a really slow internet connection—it often shows up pixelated or blotchy. A low bitrate does the exact same thing to your video. A healthy bitrate ensures that every last detail, from the subtle texture on a fabric to the complex shadows in a dark scene, comes through loud and clear.
When it comes to streaming, finding the right bitrate is a delicate balancing act. Netflix, for instance, recommends an internet speed of at least 15 Mbps for a stable 4K stream. That number isn't arbitrary; it reflects the data pipeline needed to maintain quality without constant buffering.
Color Depth: Painting with a Billion Colors
Finally, we have color depth, which defines the total number of distinct colors a video can display. Most standard videos you see online use 8-bit color, which offers a palette of roughly 16.7 million colors. While that sounds like a lot, it can sometimes cause an ugly visual problem called "color banding," where you see distinct, stepladder-like lines in a smooth color gradient, like a sunset.
This is why professional 4K productions often step up to 10-bit color, which unlocks a staggering 1.07 billion colors. This massive jump in information completely eliminates banding and produces incredibly smooth, realistic color transitions. For creators, it means richer, more true-to-life visuals that capture the world much closer to how our own eyes see it.
While most platforms default to a 16:9 widescreen format, it's the underlying color and data that truly bring that frame to life. If you're adapting your content for various screens and need to get the framing just right, you can learn more about how to convert video aspect ratio for any platform in our other guides.
The Practical Realities of a 4K Workflow
Jumping into the world of 4K video is a fantastic way to boost the quality of your work, but it’s a decision that echoes through your entire creative process. Moving from 1080p to 4K isn't just about getting more pixels on the screen; it's a huge leap in the sheer amount of data you have to wrangle at every single step, from hitting record to final delivery.
This data explosion has an immediate and very real impact on storage. We're talking about a single minute of uncompressed 4K footage easily eating up several gigabytes of space. For creators, this means a once-tidy library of project files can swell into a multi-terabyte beast almost overnight.

Hardware Requirements for a Smooth 4K Experience
If you've ever tried to scrub through a 4K timeline on a computer that wasn't ready for it, you know the pain. The experience is full of frustrating lag, choppy playback, and render times that feel like an eternity. To avoid these creative bottlenecks, your hardware needs to have some serious muscle.
When you're thinking about upgrading, it's also worth considering the real cost of editing video, because high-resolution files put a significant strain on your resources and can really stretch out project timelines.
Here's a breakdown of the components that matter most:
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): This is your computer’s engine. A powerful, multi-core processor is non-negotiable for decoding the immense amount of information packed into every 4K frame.
- Graphics Processing Unit (GPU): A strong, dedicated graphics card is your best friend. It takes the heavy lifting of rendering, effects, and smooth playback off the CPU, making everything feel snappier.
- Random Access Memory (RAM): 4K video editing is incredibly memory-hungry. You can get by with 16GB as a bare minimum, but 32GB or more is what you really want for a fluid, responsive workflow.
The storage and delivery infrastructure for 4K content presents significant technical challenges. A single 4K movie can require around 100 gigabytes of storage, but the steep drop in hard drive costs to roughly $25 per terabyte has made storing these files more practical for everyone.
The Unsung Heroes: Modern Compression Codecs
So, how is it even possible to stream a massive 4K movie without sitting through hours of buffering? The magic behind this is a set of advanced compression algorithms called codecs. They are the unsung heroes responsible for shrinking gigantic video files into something manageable enough to send over the internet.
For 4K video, the most important player is H.265, also known as High-Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC). It's a game-changer because it's about twice as efficient as its older sibling, H.264. This means it can deliver the exact same visual quality at roughly half the bitrate, which is precisely what makes 4K streaming on platforms like Netflix and YouTube possible for millions of people.
If you're grappling with the logistics of these massive files, our guide on how to upload large videos to YouTube has some practical tips that can help.
Using 4K Video to Create Better Social Media Content
At first glance, shooting in 4K for platforms like TikTok or Instagram might seem like bringing a cannon to a knife fight. After all, most people are just watching on their phones, right? But here’s a secret the pros know: starting with a 4K source file is one of the smartest moves you can make to create social content that pops.
That abundance of pixels gives you a level of creative freedom that you just can't get from a standard 1080p camera. It opens up powerful editing tricks that can elevate your videos and, believe it or not, actually save you time in the long run.
The Game-Changing Power of Reframing
The biggest win for shooting 4K for social media comes down to one word: reframing.
Let’s say you’re filming an interview with one camera set up for a wide, horizontal shot. Because your canvas is a massive 3840 x 2160 pixels, you have so much extra detail that you can digitally punch in to create entirely new shots from that single take—all without any noticeable loss in quality.
This is a lifesaver for creating vertical video. You can carve out a perfect 9:16 vertical slice from your wide shot, and it will still have more pixels than a native 1080p video. From one recording, you can create a wide shot, a medium shot, and a close-up for your Reels or Shorts. You can even create artificial camera movements, like a slow pan, all in your editing software.
Think about filming a cooking tutorial in 4K:
- The Wide Shot: You film the entire kitchen counter in one simple, horizontal 4K take.
- The Vertical Clip: In your editor, you crop a vertical 9:16 section that focuses on the host chopping vegetables.
- The Punch-In Clip: Using the exact same footage, you create a second, much tighter vertical clip showing just the close-up action of the knife and ingredients.
Just like that, you've turned one easy shot into two high-quality vertical videos. You’ve doubled your content output without setting up a second camera or spending more time on set. If you want to get into the nitty-gritty of aspect ratios, our guide on formatting videos for Instagram has you covered.
Why Downscaled 4K Looks Better Than Native 1080p
Even if you’re posting to a platform that compresses everything down to 1080p, starting with 4K footage gives you a clear visual advantage. When a 4K video is shrunk down to 1080p, the final image looks noticeably sharper and more detailed than a video that was shot in 1080p from the start.
This technique is called oversampling. You're essentially taking the rich visual data from 8.3 million pixels and intelligently compressing it into a 2.1 million pixel frame. The result is a cleaner image with truer colors and fewer compression artifacts.
It's a subtle difference, but it's what makes content look polished and professional. In a world where online video is projected to make up over 82% of all internet traffic by 2022, that extra bit of sharpness can be the very thing that stops someone from scrolling past your post. It's a simple way to make your videos look like they were made with a much bigger budget.
Answering Your Top Questions About 4K Video
Even after getting the basics down, you're bound to run into some practical questions once you start working with 4K video. This last section is all about clearing up that lingering confusion with straightforward answers to the most common queries.
Think of it as your quick-reference guide for putting all this knowledge into practice.

We'll cover everything from what kind of screen you need to whether it's worth worrying about the next big thing, making sure you walk away ready to make smart decisions with your 4K projects.
Do I Really Need a 4K Screen to Watch 4K Video?
This is one of the biggest questions we hear, and the answer isn't a simple yes or no. To see the full, glorious detail of all 8.3 million pixels, you absolutely need a 4K-capable screen. No way around that.
But here's the interesting part: watching 4K content on a 1080p screen still looks better than watching native 1080p footage. When a 4K video is downscaled to fit the smaller screen, it benefits from a process called oversampling. Essentially, you’re cramming more visual information into a smaller space, which results in a noticeably sharper, cleaner image.
So, while a 4K screen is essential for the true 4K experience, you can still perceive a quality boost on a 1080p screen. You'll get some of the benefit, but not all of it.
Is 4K Worth It for Small Screens Like a Phone?
For pure viewing? Honestly, not really. On a small smartphone screen, the pixel density is already so high that the human eye can barely tell the difference between 1080p and 4K. The extra detail just gets lost.
The real value of 4K for mobile is on the creation side. Shooting in 4K gives you incredible flexibility. You can crop, zoom, and reframe your shots in post-production without losing any quality. This is a massive advantage for turning a single horizontal video into multiple vertical clips for social media.
How Much Faster Does My Internet Need to Be for 4K?
Streaming 4K video demands a much healthier internet connection than HD does. Since you're pulling down four times the pixel data, your bandwidth has to be up to the task to avoid that dreaded buffering wheel.
Let’s look at what a service like Netflix recommends:
- HD (1080p) Streaming: Needs a steady 5 megabits per second (Mbps).
- 4K (UHD) Streaming: Jumps up to a recommended speed of at least 15 Mbps.
That means you need a connection that's consistently three times faster for a smooth 4K stream. And if you live in a house where multiple people are online, a 50 Mbps plan (or higher) is a much safer bet to keep everyone happy.
Can My Old TV Play 4K Content?
Unfortunately, no. A TV’s native resolution is built into its hardware. An older 1080p television has a physical grid of 1920 x 1080 pixels and simply can’t display the 3840 x 2160 pixels of a 4K signal. It just doesn't have enough little dots of light.
To get the real deal, you need a display specifically sold as a 4K or UHD TV. You'll also need a 4K source device—like a 4K Blu-ray player, a new gaming console, or a streaming box like an Apple TV 4K or Chromecast with Google TV—connected with an HDMI 2.0 cable or newer.
What’s the Future of Video Resolution Beyond 4K?
The next big leap is 8K, which boasts a mind-boggling 7680 x 4320 pixel count. That's four times the detail of 4K and a whopping sixteen times that of 1080p.
While you can buy 8K TVs today, the content is still incredibly rare. More importantly, the visual upgrade from 4K to 8K is a case of diminishing returns for most people on normal-sized screens.
Right now, more exciting advancements are happening in other areas. Technologies like High Dynamic Range (HDR), which creates far better contrast and more vibrant colors, are making a much bigger, more noticeable impact on the viewing experience than just cramming in more pixels.
Ready to transform your long-form 4K videos into engaging social media clips effortlessly? Our AI-powered platform helps you create high-impact shorts for TikTok, Reels, and YouTube 10x faster. We provide automated editing, animated captions, and a streamlined content repurposing workflow that gives you a significant advantage in speed and efficiency. Get started with Swiftia for free and see the difference for yourself.


